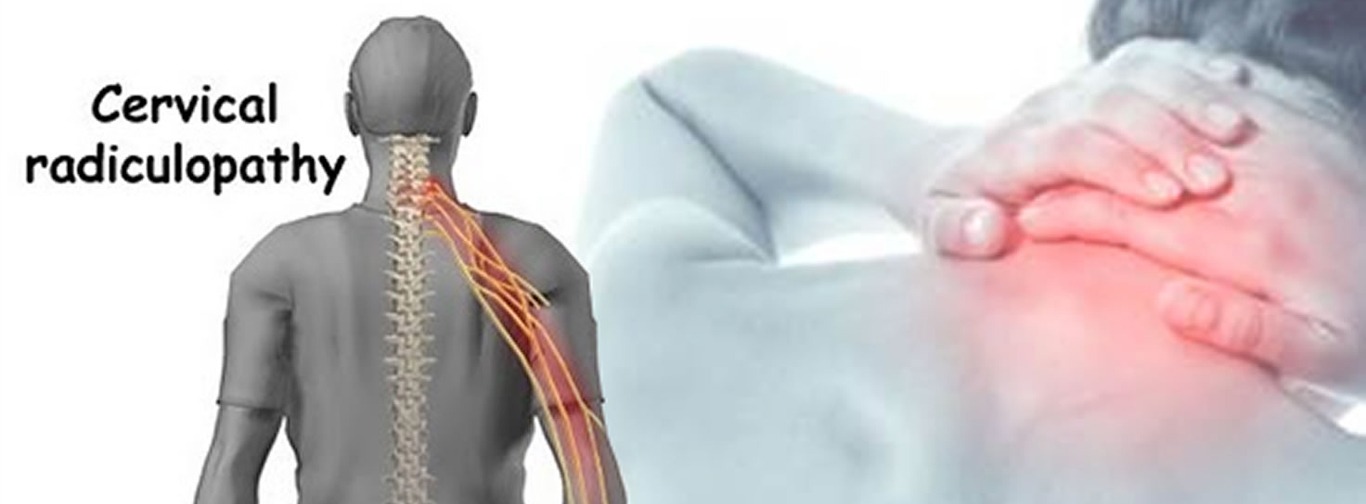
Cervical Spondylosis
Cervical spondylosis is extremely common. More than 85% of people over the age of 60 are affected. The condition most often causes pain and stiffness in the neck — although many people with cervical spondylosis experience no noticeable symptoms. In most cases, cervical spondylosis responds well to conservative treatment that includes medication and physical therapy.
For most people, cervical spondylosis causes no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they typically include pain and stiffness in the neck. This pain can range from mild to severe. It is sometimes worsened by looking up or looking down for a long time, or by activities in which the neck is held in the same position for a prolonged period of time — such as driving or reading a book. The pain usually improves with rest or lying down.
In most cases, treatment for cervical spondylosis is nonsurgical.Physical therapy. Physical therapy is usually the first nonsurgical treatment that your doctor will recommend. Specific exercises can help relieve pain, as well as strengthen and stretch weakened or strained muscles. In some cases, physical therapy may include posture therapy or the use of traction to gently stretch the joints and muscles of your neck.
